Young Researcher Paper Award 2023
🥇Winners
🥇Winners
Print: ISSN 0914-4935
Online: ISSN 2435-0869
Sensors and Materials
is an international peer-reviewed open access journal to provide a forum for researchers working in multidisciplinary fields of sensing technology.
Online: ISSN 2435-0869
Sensors and Materials
is an international peer-reviewed open access journal to provide a forum for researchers working in multidisciplinary fields of sensing technology.
Tweets by Journal_SandM
Sensors and Materials
is covered by Science Citation Index Expanded (Clarivate Analytics), Scopus (Elsevier), and other databases.
Instructions to authors
English 日本語
Instructions for manuscript preparation
English 日本語
Template
English
Publisher
MYU K.K.
Sensors and Materials
1-23-3-303 Sendagi,
Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0022, Japan
Tel: 81-3-3827-8549
Fax: 81-3-3827-8547
MYU Research, a scientific publisher, seeks a native English-speaking proofreader with a scientific background. B.Sc. or higher degree is desirable. In-office position; work hours negotiable. Call 03-3827-8549 for further information.

MYU Research
(proofreading and recording)

MYU K.K.
(translation service)

The Art of Writing Scientific Papers
(How to write scientific papers)
(Japanese Only)
is covered by Science Citation Index Expanded (Clarivate Analytics), Scopus (Elsevier), and other databases.
Instructions to authors
English 日本語
Instructions for manuscript preparation
English 日本語
Template
English
Publisher
MYU K.K.
Sensors and Materials
1-23-3-303 Sendagi,
Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0022, Japan
Tel: 81-3-3827-8549
Fax: 81-3-3827-8547
MYU Research, a scientific publisher, seeks a native English-speaking proofreader with a scientific background. B.Sc. or higher degree is desirable. In-office position; work hours negotiable. Call 03-3827-8549 for further information.

MYU Research
(proofreading and recording)

MYU K.K.
(translation service)

The Art of Writing Scientific Papers
(How to write scientific papers)
(Japanese Only)
Sensors and Materials, Volume 31, Number 11(4) (2019)
Copyright(C) MYU K.K.
Copyright(C) MYU K.K.
|
pp. 3859-3870
S&M2055 Research Paper of Special Issue https://doi.org/10.18494/SAM.2019.2589 Published: November 30, 2019 Spatial Clustering of Seoul’s Elderly Captive Riders Using Smart Card Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis [PDF] Junhyung Lee and Jaekang Lee (Received August 31, 2019; Accepted November 19, 2019) Keywords: spatial autocorrelation, elderly, smart card, big data, social service
Smart card transactions contain user information and travel patterns. Thus, in this study, elderly smart card transactions were analyzed to determine elderly captive riders’ hot spots that need appropriate social services for them. There has been minimal focus on the spatial autocorrelation of smart card big data when developing new traffic policies. Therefore, in this study, spatial autocorrelation analysis was performed using Seoul’s smart card data for six weeks. In the collected data, it was found that 76.3% of the elderly trips were concentrated on subways, which offer free tickets. For this reason, we examined elderly captive bus riders in this study. Moran’s I was 0.277 for the elderly smart card transactions, and it has a positive spatial autocorrelation with the significance level of 0.01. Local indicators of spatial association (LISA) analysis is used to determine the spatially autocorrelated areas. Fifty administrative units (dongs) in Seoul were considered hot spots, and spatial clustering was confirmed; 61 dongs were considered cold spots. The distributions of hot spots and cold spots seem to be closely related to the subway supply level rather than the elderly population. Twenty-eight hot spots seriously need appropriate social services for elderly bus users because those hot spots do not operate subway service. First, barrier-free bus stops should be installed at the 28 hot spots. Second, bus lines that pass the 28 hot spots need to have high priority when supplying low-floor buses. Third, the low-floor bus shuttle service from/to the 28 hot spots is proposed by analyzing the top nine origins and destinations of the elderly. To propose advanced public transportation policies for the elderly, smart card spatial autocorrelation analysis can be used.
Corresponding author: Junhyung Lee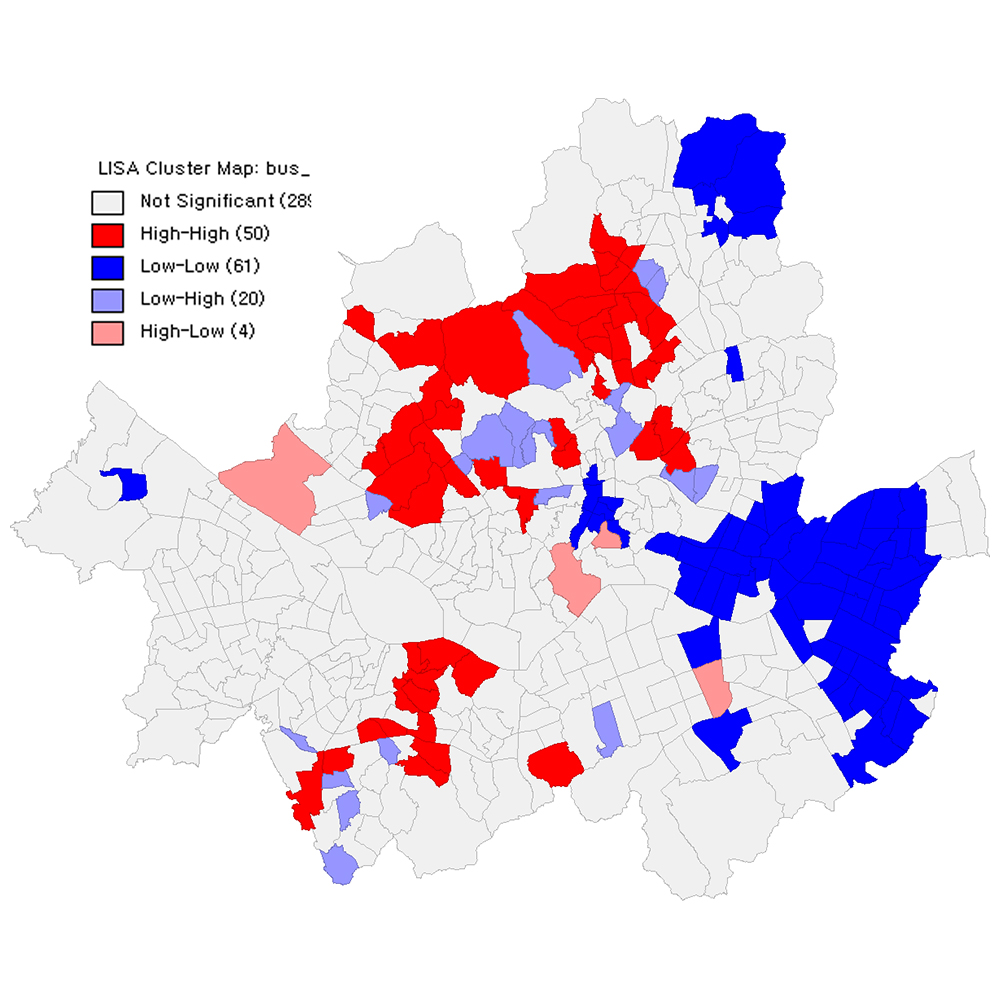  This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Cite this article Junhyung Lee and Jaekang Lee, Spatial Clustering of Seoul’s Elderly Captive Riders Using Smart Card Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis, Sens. Mater., Vol. 31, No. 11, 2019, p. 3859-3870. |
Forthcoming Regular Issues
Forthcoming Special Issues
Applications of Novel Sensors and Related Technologies for Internet of Things
Guest editor, Teen-Hang Meen (National Formosa University), Wenbing Zhao (Cleveland State University), and Cheng-Fu Yang (National University of Kaohsiung)
Call for paper
Special Issue on Advanced Data Sensing and Processing Technologies for Smart Community and Smart Life
Guest editor, Tatsuya Yamazaki (Niigata University)
Call for paper
Special Issue on Advanced Sensing Technologies and Their Applications in Human/Animal Activity Recognition and Behavior Understanding
Guest editor, Kaori Fujinami (Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology)
Call for paper
Special Issue on International Conference on Biosensors, Bioelectronics, Biomedical Devices, BioMEMS/NEMS and Applications 2023 (Bio4Apps 2023)
Guest editor, Dzung Viet Dao (Griffith University) and Cong Thanh Nguyen (Griffith University)
Conference website
Call for paper
Special Issue on Piezoelectric Thin Films and Piezoelectric MEMS
Guest editor, Isaku Kanno (Kobe University)
Call for paper
Special Issue on Advanced Micro/Nanomaterials for Various Sensor Applications (Selected Papers from ICASI 2023)
Guest editor, Sheng-Joue Young (National United University)
Conference website
Call for paper
-
For more information of Special Issues (click here)
-
Special Issue on Advanced Micro/Nanomaterials for Various Sensor Applications (Selected Papers from ICASI 2024)
- Accepted papers (click here)
- A Prototype Portable Voltammetric Sensor for Determining Titratable Acidity of Sake and Moromi
Akira Kotani, Kokoro Taniguchi, Koichi Machida, Kazuhiro Yamamoto, and Hideki Hakamata - PACKTEST for L-Glutamate Quantification: Development of On-site and High-throughput Analytical Kits using L-Glutamate Oxidase Mutant
Keita Murai, Hiroki Yamaguchi, Satoru Furuuchi, Kazutoshi Takahashi, Uno Tagami, Moemi Tatsumi, Toshimi Mizukoshi, Hiroshi Miyano, Shuntaro Okauchi, and Masayuki Sugiki - Development of Portable Multi-fluorescence Detection System Using Indium Tin Oxide Heater for Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification
Ryo Ishii, Sota Hirose, Shoji Yamamoto, Kazuhiro Morioka, Akihide Hemmi, and Hizuru Nakajima - Reproduction of Absorption Spectra of Bromothymol Blue–Methyl Red Mixed Indicator from RGB and L*a*b* Color Coordinates and Application to Fast Spectrum Acquisition
Yusuke Kimura, Arinori Inagawa, and Nobuo Uehara - Orthogonality of α-Sulfoquinovosidase in Human Cells and Development of Its Fluorescent Substrate
Ryosuke Yoshida, Ryosei Kaguma, Ryosuke Kaneko, Ichiro Matuso, Makoto Yoritate, Go Hirai, Takamasa Teramoto, Yoshimitsu Kakuta, Kosuke Minamihata, Noriho Kamiya, Teruki Nii, Akihiro Kishimura, Takeshi Mori, and Yoshiki Katayama
- A Prototype Portable Voltammetric Sensor for Determining Titratable Acidity of Sake and Moromi
- Accepted papers (click here)
- Healthcare System from Multisensor Collaboration and Human Action Recognition
Hongwei Gao, Xuna Wang, Zide Liu, and Yueqiu Jiang
- Healthcare System from Multisensor Collaboration and Human Action Recognition
Guest editor, Sheng-Joue Young (National United University)
Conference website
Call for paper
Special Issue on Asia-Pacific Conference of Transducers and Micro-Nano Technology 2024 (APCOT 2024)
Guest editor, Guangya ZHOU (National University of Singapore) and Chengkuo LEE (National University of Singapore)
Conference website
Call for paper
Special Issue on Sensing and Information and Communication Technologies toward Non-intrusive, Undisturbed, and Calm Healthcare Monitoring
Guest editor, Kosuke Motoi (Shizuoka Institute of Science and Technology)
Call for paper
Special Issue on Innovative Approaches to Forest Monitoring Using Sensing Techniques
Guest editor, Heesung Woo (Kangwon National University)
Call for paper
Special Issue on Sensor for Society
Guest editor, Arinori Inagawa (Utsunomiya University), Yukiko Moriiwa (Tokyo University of Pharmacy and Life Sciences), and Atsushi Shoji (Tokyo University of Pharmacy and Life Sciences)
Call for paper
Special Issue on Materials, Devices, Circuits, and Analytical Methods for Various Sensors (Selected Papers from ICSEVEN 2023)
Guest editor, Chien-Jung Huang (National University of Kaohsiung), Mu-Chun Wang (Minghsin University of Science and Technology), Shih-Hung Lin (Chung Shan Medical University), Ja-Hao Chen (Feng Chia University)
Special Issue on Materials, Devices, Circuits, and Analytical Methods for Various Sensors (Selected Papers from ICSEVEN 2024)
Guest editor, Chien-Jung Huang (National University of Kaohsiung), Mu-Chun Wang (Minghsin University of Science and Technology), Shih-Hung Lin (Chung Shan Medical University), Ja-Hao Chen (Feng Chia University)
Conference website
Call for paper
Special Issue on Sensing and Data Analysis Technologies for Living Environment, Health Care, Production Management, and Engineering/Science Education Applications (2023)
Guest editor, Chien-Jung Huang (National University of Kaohsiung), Rey-Chue Hwang (I-Shou University), Ja-Hao Chen (Feng Chia University), Ba-Son Nguyen (Lac Hong University)
Special Issue on Sensing and Data Analysis Technologies for Living Environment, Health Care, Production Management, and Engineering/Science Education Applications (2024)
Guest editor, Chien-Jung Huang (National University of Kaohsiung), Rey-Chue Hwang (I-Shou University), Ja-Hao Chen (Feng Chia University), Ba-Son Nguyen (Lac Hong University)
Call for paper
Special Issue on 2D Materials-based Sensors and MEMS/NEMS
Guest editor, Kazuhiro Takahashi (Toyohashi University of Technology)
Call for paper
Special Issue on Biosensing Technology Using Micro- and Nanostructures
Guest editor, Kazuhiro Morioka and Atsushi Shoji (Tokyo University of Pharmacy and Life Sciences)
Call for paper
Special Issue on Advanced Sensors Materials and Processes
Guest editor, Shih-Chen Shi (National Cheng Kung University) and Tao-Hsing Chen (National Kaohsiung University of Science and Technology)
Call for paper
Special Issue on Advanced Sensing Technologies for Green Energy
Guest editor, Yong Zhu (Griffith University)
Call for paper
Special Issue on Spatial Information and Digital Twins for Built Environment Development
Guest editor, Dong Ha Lee (Kangwon National University), Myeong Hun Jeong (Chosun University), Jaekang Lee (Dong-A University), Jisoo Park (Indiana State University), and Sungjin Kim (Hanbat National University)
Call for paper
Special Issue on Mobile Computing and Ubiquitous Networking for IoT Society
Guest editor, Takuya Yoshihiro (Wakayama University) and Shigemi Ishida (Future University Hakodate)
Call for paper
Special Issue on Intelligent Sensing and Analysis for Human–Machine Interaction in Healthcare, Biomedical Engineering, and Human-Centered Industrie
Guest editor, Dalin Zhou (University of Portsmouth), Jiahui Yu (Zhejiang University), Yuichiro Toda (Okayama University), and Zhaojie Ju (University of Portsmouth)
Call for paper
Special Issue on Multisource Sensors for Geographic Spatiotemporal Analysis and Social Sensing Technology
Guest editor, Prof. Xiang Lei Liu (Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture) and Prof. Bogang Yang (Beijing Institute of Surveying and Mapping)
Call for paper
Special Issue on Geomatics Technologies for the Realization of Smart Cities
Guest editor, Prof. He Huang (Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture) and Prof. Junxing Yang (Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture)
Call for paper
Special Issue on New Functions of Micro/Nanomaterials and Devices
Guest editor, Takahiro Namazu (Kyoto University of Advanced Science)
Call for paper
Special Issue on Smart Sensing Approaches for Low Carbon, Energy-efficient Manufacturing Processes
Guest editor, Cheng-Chi Wang (National Sun Yat-sen University)
Call for paper
Special Issue on Smart Sensors for Chemical and Agriculture Applications
Guest editor, Kazuaki Sawada (Toyohashi University of Technology)
Call for paper
- Accepted papers (click here)
Copyright(C) MYU K.K. All Rights Reserved.
